Ankle Arthritis: Ankle Joint Pain, Swelling, Deformity, & Instability
The ankle is a complex structure that carries the body’s weight. The joint and the ligament connections facilitate movement and are crucial for daily activities like walking, running and jumping.
Trauma from accidents or sports-related injuries can lead to the development of ankle arthritis. A patient suffering from this condition will experience pain while performing basic movements of the ankle, thus severely restricting mobility.
In most cases of minor injuries, sufficient rest and conservative medical treatment can help heal the ankle.
However, chronic cases of repeated trauma or long term degeneration can lead to severe complications that require non-conservative, i.e. surgical treatment.

Ankle Arthritis Symptoms
The ligaments in the ankle joint serve as shock absorbers and bear our weight during movement. Unconventional movement or trauma can lead to ankle arthritis. It is a sign of wear and tear that leads to long term degradation and reduction in the joint space.
Some of the commonly associated symptoms include:
- Pain from stressing the ankle, for example standing up or walking.
- Radiating pain in the foot and lower leg.
- Stinging pain when walking on uneven terrain and when tipping sideways.
- Stiffening in the ankle.
In chronic cases, the cartilage between the upper and lower ankle bones is worn out completely and the buffer between the bones is lost. This causes the bones to rub against each other.
A patient’s joint is severely compromised and lacks stability. The skin in the area turns red and this can be associated with inflammation. In some cases, new bone forms on the edge of the joint which leads to movement restrictions as the disease progresses.
Immediate professional medical attention is highly advised.
*Note: Ankle Arthrosis is not a sign of aging. It is most commonly a delayed consequence of an injury to the ankle, such as a supination trauma which was not treated properly. In some rare cases, metabolic diseases such as gout or rheumatism can lead to ankle arthrosis.
Diagnosis of Ankle Arthritis
A complete medical examination by a professional orthopedist is the best course of action in case of ankle arthritis. The physician begins with a complete history of the circumstances of the accident and injury.
Sophisticated imaging technology like X-rays and MRI’s can be used to detect the true extent of injury to the individual parts of the ankle joint and to detect bone extensions.
A quick synovial fluid test can check for the presence of free joint bodies as well as cartilage fragments.
It is crucial to understand the extent of the trauma and the progression of the degeneration to formulate the most efficient treatment path.

Ankle Arthritis Treatment
Ankle arthritis treatment is mostly conservative i.e. non-surgical in the early stages of the condition. In case of direct trauma to the ankle joint, treatment begins with addressing the primary symptoms of the condition with relieving stress and providing ample rest.
-
Immobilization
Lifting pressure off the injured foot is the best first measure in case of trauma. It prevents excess stress on the injury. Ample rest and suspension of the ankle using a medical ankle is highly recommended and can facilitate a swift recovery.
-
Cooling
Applying a cool surface like an ice pack is highly effective in managing the edema caused by the injury. It soothes the joint and can provide relief to the patient.
-
Prescription Painkillers
Patients with ankle arthritis experience pain and discomfort due to the condition. Prescribed painkillers like Ibuprofen can help manage the pain and provide some relief. However, as with many medications, tolerance may occur where the effectiveness of the drugs decrease as well as other potential side effects.

-
Prescribed Physiotherapy
In cases of ankle arthritis, rehabilitation is very important to ensure complete healing and to manage the long term consequences of the condition.
Prescribed physiotherapy, with the use of ankle braces, help strengthen the ligaments in the ankle that have lost stability. The aim is to delay the wear and tear of the joint and potentially repair the damage.
In cases of degeneration of muscle due to long periods of fixation like in a plaster, physiotherapy helps a patient regain mobility.
-
Surgical Intervention
In patients with advanced symptoms, cortisone injections alongside surgical intervention sometimes become necessary. The compromised ligaments can no longer act as an efficient buffer between the bones in the ankle and might need surgery to facilitate healing. Surgery might be required if there are bone growths in the joint.

-
Medical Ankle Braces
Ligaments and muscles need several months of ample rest and support to regain strength and stability. During this time, a medical ankle brace supports the ankle.
They are crucial in the immobilization phase of treatment and provide much-needed support to the compromised joint. The brace helps reduce the strain on the ankle as well as reduces the formation of edema.
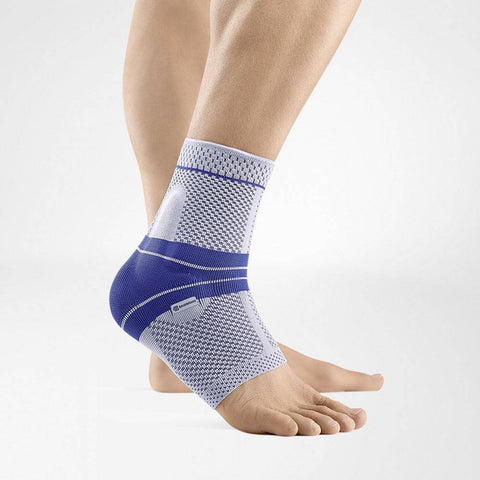
ORTHOSIS: Prevention of Ankle Arthritis
Ankle braces are valuable tools in both the complete healing of the ankle joint after injury or trauma, as well as prevention of the progression of long term osteoarthritis.
Braces like the MalleoTrain help secure the ankle and provide much-needed support and stability. The brace encourages good proprioception and helps prevent unnatural stress on the ankle making it crucial in managing the condition.
The MalleoTrain features two pads that massage the ankle and provide relief from pain. The medical-grade compression stimulates blood circulation and reduces the formation of edema. The breathable, hypoallergenic material is flexible, making it comfortable and supportive to wear for extended periods.