Symphysis Pubis Dysfunction (SPD): Discomfort in the Pelvic Region
The pelvis is a protective structure for the internal organs, but it also plays a vital part as a supportive structure for the body particularly in an upright position and with walking.
The ring-shape of the pelvis, along with the support of the pelvic ligaments and pelvic floor muscles, makes it strong and stable. Two joints at the back connect the pelvis to the sacrum (the base of the spine) which are called sacroiliac joints.
At the front of the pelvis, the left and right pubic bones are joined with cartilage to form the pubic symphysis, where only the slightest degree of movement can occur.
Pubic Bone Pain in Pregnancy
Pain at the front of the pelvis or pubic bone is known as pubic symphysis pain and it is a common condition to occur during and after pregnancy. It can affect up to ten percent of pregnant women, as well as anyone engaging in strenuous physical activity.

Causes of Symphysis Pubis Dysfunction
If an excessive movement occurs at the pubic symphysis, it can become loose. During pregnancy, in particular, normal hormonal changes lead to increased laxity of the ligaments around the pelvis, which can cause the pubic symphysis to widen.
This loosening of the pubic symphysis can be very painful. Due to the nature of the ring structure of the pelvis, laxity at the pubic symphysis can affect the sacroiliac joints, causing an overall instability of the pelvis. Consequently, symptoms can often include low back pain.
Pubic Symphysis pain is most common in pregnant women, however, it can affect anyone engaging in more strenuous physical activity. The most common causes are:
Symphysis Pubis Dysfunction During Pregnancy
- Taking large strides or overextending the legs while in the later stages of pregnancy (2nd and 3rd trimesters).
- Women during and after pregnancy are at increased risk, and even simple movements can cause this issue.

Sporting Injury or Trauma
- Anyone playing sports can suffer from this injury. A slip, trip, big jump or overloading the pelvis can loosen the pubic symphysis in both men and women.
- A sporting trauma or activities with postures that put pressure on the pelvis, such as cycling, can also create pubic symphysis loosening, which may lead to pubic symphysis pain and a marked restriction of movement.
Symphysis Pubis Dysfunction Symptoms
Pubic symphysis loosening can produce different degrees of symptoms depending on its severity.
In mild cases, the loosening creates pain that is mainly noticeable at the pubic bone.
In more severe cases with further loosening, pain can be more intense and cause greater restrictions to activities of daily life.
- Getting up, bending over, walking up stairs, lifting a heavy object or lying on your side is typically very painful or potentially impossible to do.
- With pregnancy, symptoms commonly deteriorate as the pregnancy progresses, and the birth itself can further stretch (or in extreme cases completely rupture) the pubic symphysis.
Treatment of Symphysis Pubis Dysfunction (Pubic Bone Pain)
Treating pubic symphysis pain is focused on preventing the progression of pubic symphysis loosening and stabilizing the sacroiliac joints for pain relief. These range from simple at-home remedies to medical intervention.
-
Physical Therapy

-
Surgery
Surgery may be an option for a torn pubic symphysis in more severe cases when such an injury has been medically diagnosed with X-ray or MRI imaging. This is a last case option and is avoided in most instances unless absolutely necessary.
-
Bracing
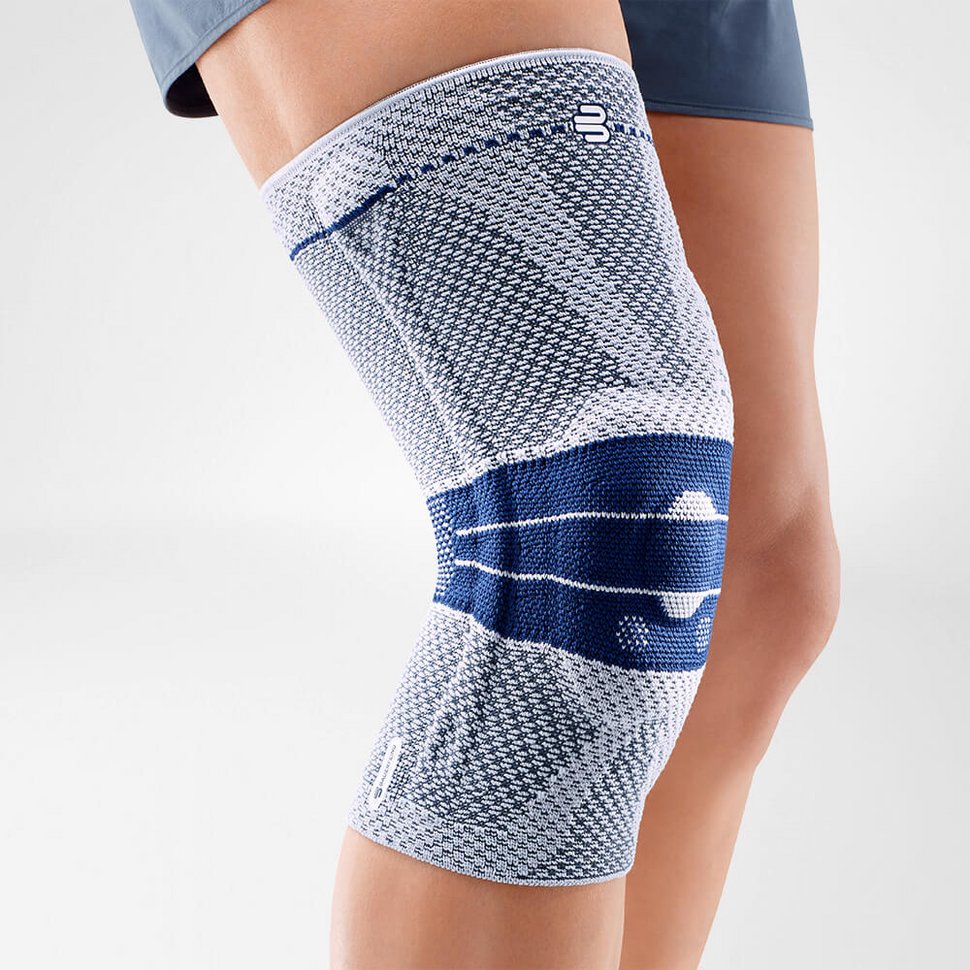
Medical support braces (orthoses) are effective measures of providing pelvic ring stability in cases of pubic symphysis loosening. Bauerfeind provides bracing options clinically designed and proven specifically for such an injury, such as the SacroLoc.
-
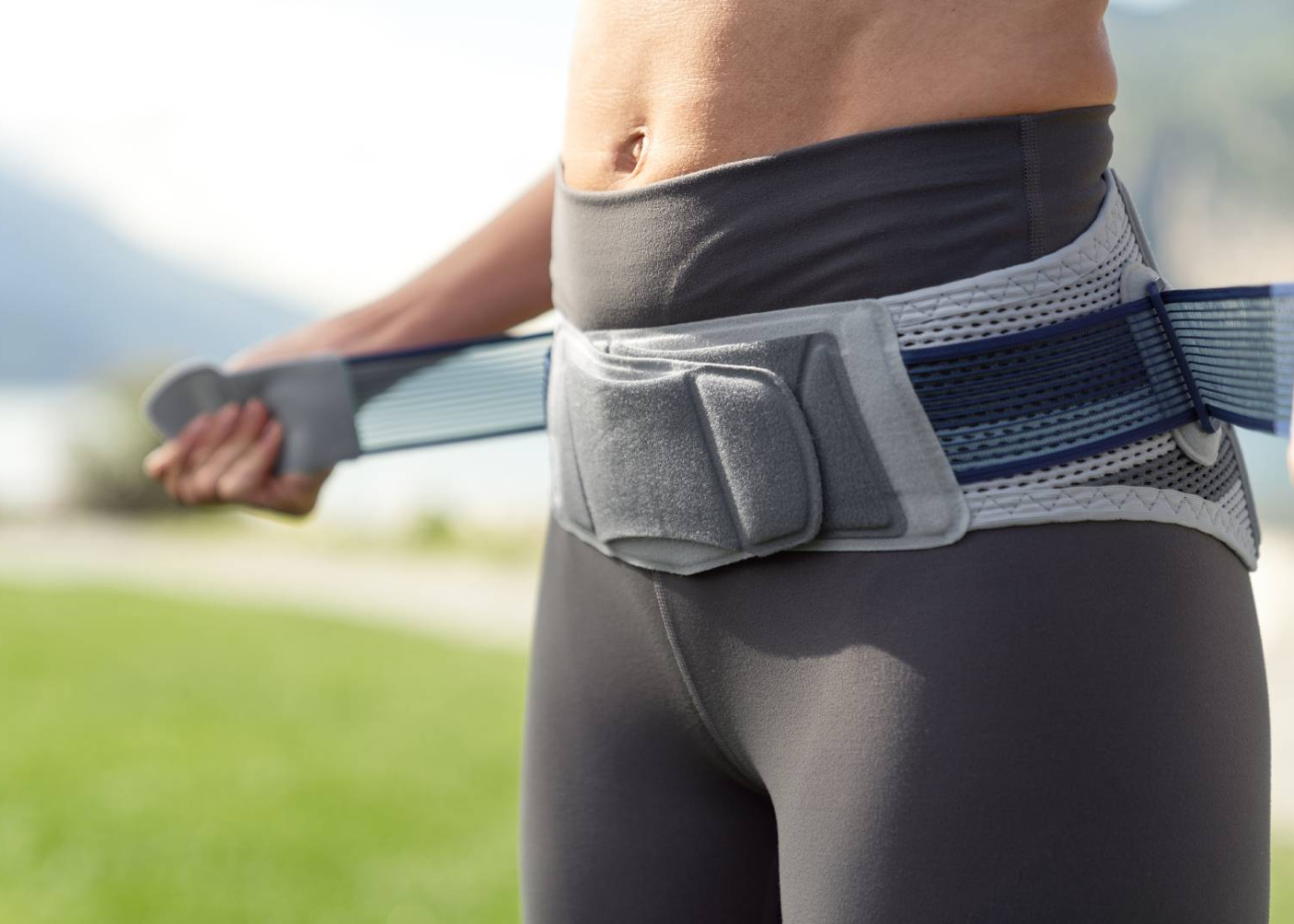
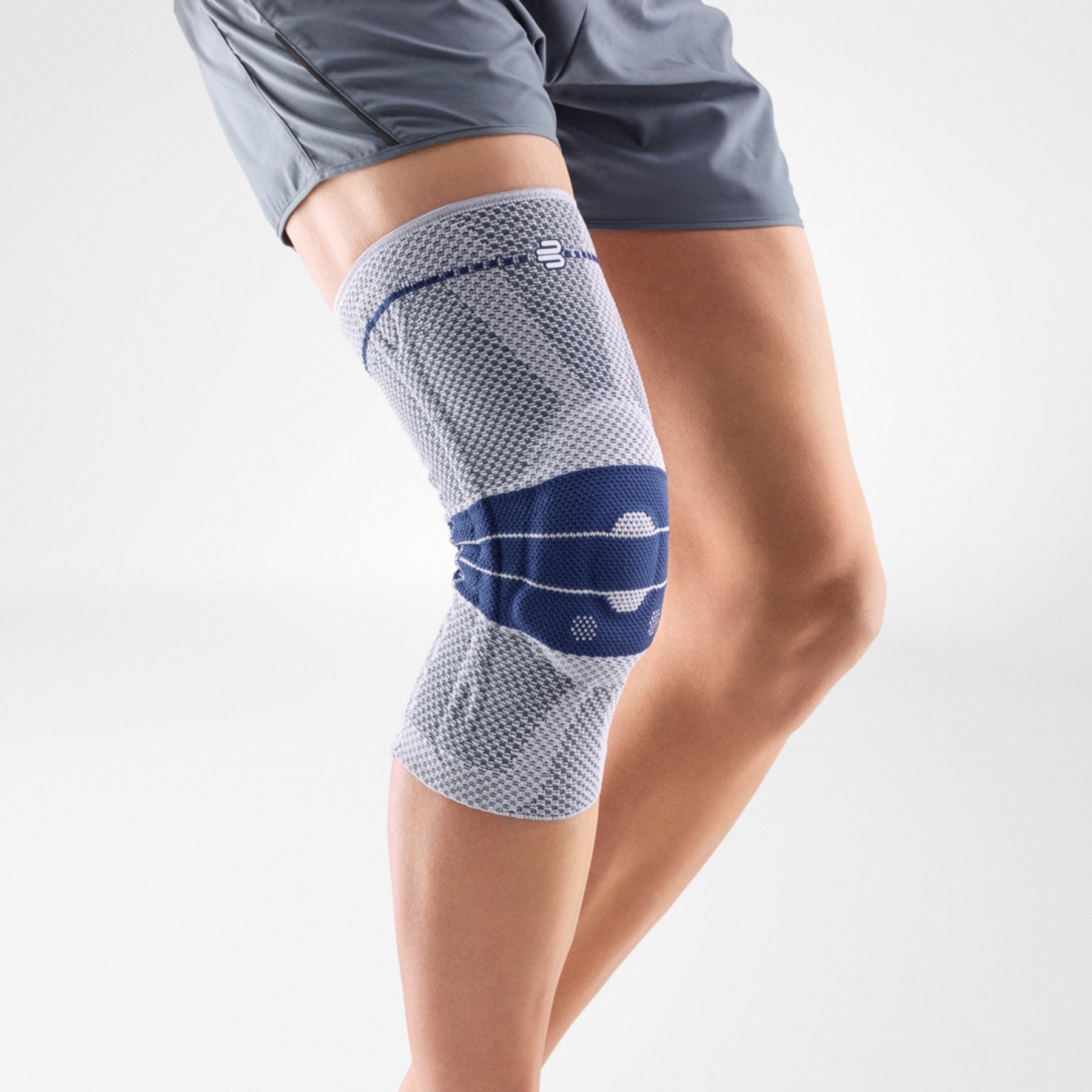
Sacroloc Back Brace
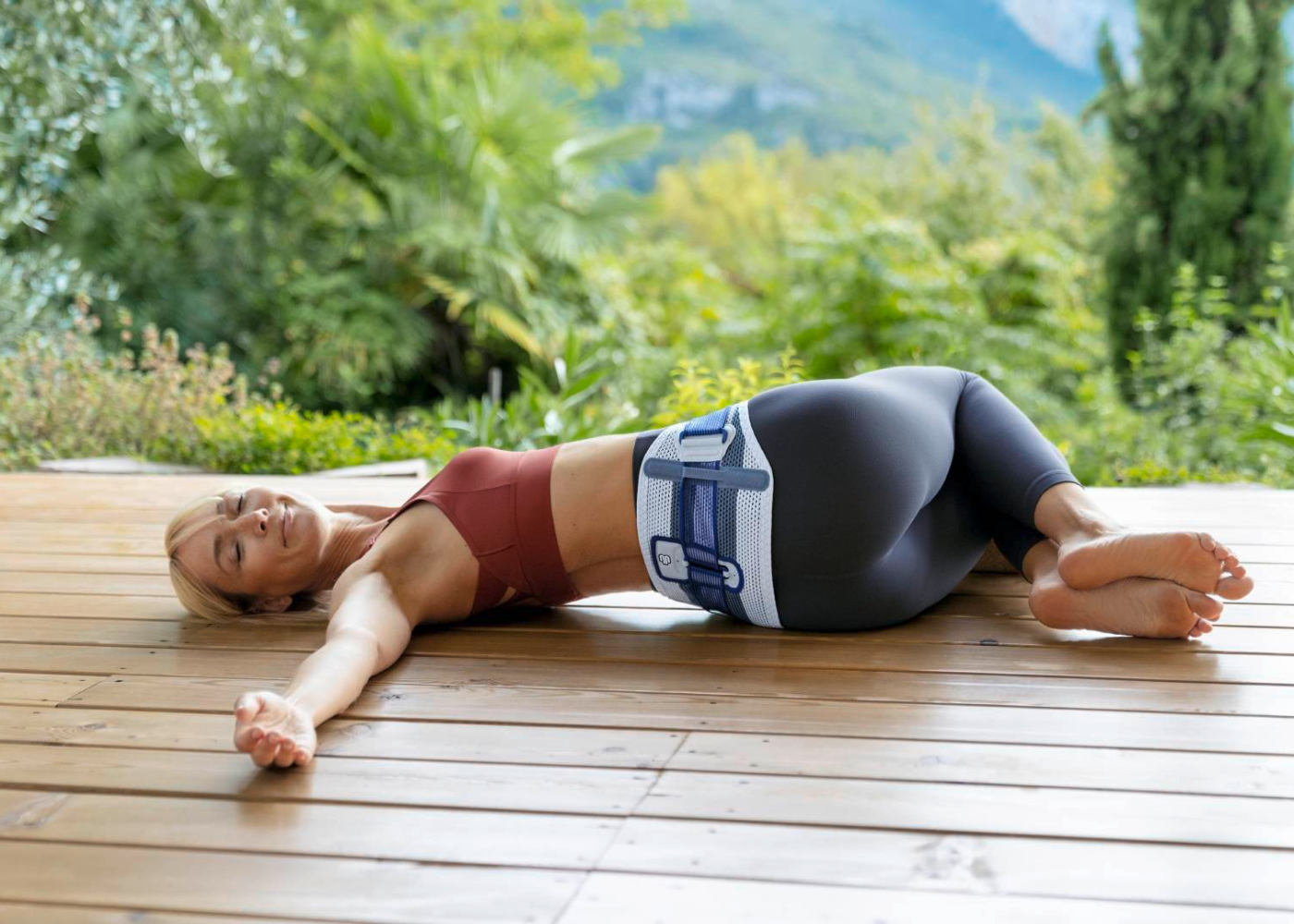
The SacroLoc is a support brace (orthosis) that is beneficial to recovery and healing, both during the acute phase of pubic symphysis pain for symptom relief, and as a long-term preventative aid for pelvic ring support.
While it provides support, it simultaneously massages the muscles, tendons and ligaments around the pelvis to minimize tension.
The SacroLoc is made from a breathable fabric and is designed to be flexible to a range of body shapes, making it easy to put on and comfortable to wear, whether sitting down all day or moving about.
The stabilizing tension is easily adjusted using a dual tension system, allowing the wearer to control exactly how much tension and support is provided throughout the day.

The SacroLoc has been clinically proven* to help bring relief and comfort to sufferers of pubic symphysis and sacroiliac joint pain and is used across the world for patients from Post pregnancy to Olympic athletes.
* Sichting et al.; Pelvic Belt Effects on Sacroiliac Joint Ligaments: A Computational Approach to Understand Therapeutic Effects of Pelvic Belts, Pain Physician 2014; Vol. 17: pp. 43–51 • ISSN 1533-3159
* Soisson O, Lube J, Germano A, Hammer K-H, Josten C, Sichting F, Winkler D, Milani T L, Hammer N; Pelvic Belt Effects on Pelvic Morphometry, Muscle Activity and Body Balance in Patients with Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction; PLoS ONE 10(3): e0116739. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0116739