What is Hip Arthritis (Osteoarthritis/ Coxarthroses)?
Long Term Degeneration of the Hip Joint
The hip joint connects our pelvis to the upper femur (upper leg bone). This joint facilitates the transfer of power from the upper body to the lower body, which allows for movement. Long term degeneration of the hip joint can lead to hip osteoarthritis or coxarthrosis.
In mild cases of this condition, a patient may experience pain in the hip and groin regions when walking, bending or descending stairs. Conservative therapy can help manage the progression of the disease.
However, in chronic cases where long term degeneration is apparent, surgical intervention might become necessary.

Causes of Hip Arthritis
Contrary to belief, osteoarthritis of the hip is not exclusively a disease of aging. Other risk factors that can lead to the development of the disease include:
- Physical trauma from an accident or sporting injury.
- Excessive repeated strain on the hip from rigorous physical activity through unhealthy exercise or manual labor.
- Inherent malpositions in the structure of the hip joint, as seen in hip dysplasia.
- Pre-existing conditions, such as inflammatory joint diseases like rheumatism or gout disease.
- Metabolic and weight-related diseases like obesity.
Hip Arthritis Symptoms
Hip Arthritis is a serious condition that progresses with time and age. The symptoms typically get worse and need more drastic measures to keep the hip joint from deteriorating further. Associated symptoms of hip arthritis consist of:
- The patient increasingly suffers from pain in the hip and groin area when the joint is stressed.
- The initial symptoms are limited to being painful under stress but soon progresses from episodic to constant sharp pain.
- A patient’s mobility is severely restricted and any movement like walking, bending or descending stairs is very painful.
- Swelling may occur in the hip joint.
Chronic Case Symptoms of Hip Arthritis
In chronic cases, the long-term wear and tear of the cartilage reduce the joint gap between the pelvis and the femur. This eventuates to the bones grinding against each other, and in the worst-case scenario, the entire cartilage can be compromised.
Bony growths, called osteophytes, may develop in the gap and alter the structure of the joint entirely. Consequently, the hip becomes very stiff and the patient will experience pain in both the hip and groin regions.
How to diagnose arthritis in your hip?
The diagnosis of hip arthritis is difficult in its early stages and is often neglected. Delayed treatment can cause irreversible damage to the hip. Thus, it is highly recommended to seek professional medical treatment as soon as possible.
Hip Arthritis X-Ray
- A physician begins with a complete patient history and a thorough physical examination. Sophisticated imaging technology, like X-rays and MRI’s, can help detect abnormalities in the structure of the hip joint and also get a clear idea of the progression of the disease.
In later stages of hip arthritis, changes in the joint structures are visible in these images. An effective treatment path can be decided once a deeper understanding of the severity of the condition is gained.
Hip Arthritis Treatment
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip depends on the severity and the progression of the disease.
In the case of inherent malpositions, these are typical:
For infants, corrections are made when malpositions are detected at birth. A splint is used to realign the structure and is proven effective in fixing the hip at an early age. The fixed hip does not bother the baby and is perfectly safe.
For adults, treatment for malpositions is handled through stabilization and strengthening the muscles of the hip. Hip Arthritis treatment aims to slow the progression of degeneration and alleviate pain.
A good plan of action involves:
-
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes in the early stages can help slow the progression of the condition. Avoiding stressful activities, like intensive manual labor and vigorous exercise, is an effective measure a patient can take in their daily life.
Healthy nutrition and weight can help reduce the weight resting on the hip joint and is beneficial in managing arthrosis.
-
Rehabilitation And Physiotherapy
Regulated physiotherapy helps with weight loss and targeted muscle building and is a proven effective treatment path. The prescribed exercises can help promote reorganization within the muscles and are the most effective option to curb the disease. Encouraging healthy proprioception and muscle strengthening helps prevent long term degeneration and can slow the progression of coxarthrosis. It is crucial to involve exercise and physiotherapy for a complete treatment path.

-
Heat Application
Applying heat, through the use of heat pads, has shown to alleviate pain in the muscles around the hip joint. Heat application, in combination with remedial massage and hydrotherapy, can be effective in managing pain and swelling.
-
Prescribed Pain Medication for arthritis in the hip
Medication, such as Ibuprofen or Paracetamol, can be used to help alleviate pain and swelling caused by coxarthrosis. Anti-inflammatory medication can be used to effectively manage the symptoms however only temporarily treat the pain without addressing the underlying condition. In addition, tolerance may occur where the effectiveness of the drugs decrease as well as other potential side effects.
-
Medical Hip Orthosis and Braces
It is highly recommended that ample support to the hip region is provided through the use of a medical back brace. The targeted compression and support that braces provide can help boost stability and muscle activation and reduce the possibility of further injury. Additionally a comfortable and well designed back brace should also reduce the need for reliance on painkillers with medical studies* showing by up to 52% as well as 4.8 fewer sick days due to back pain. Bauerfeind’s back braces, like the SofTec Coxa, help to compensate for the weak hip and provide much-needed stability.
-
Surgical Intervention
Operative surgery is considered only in extreme cases where symptoms are persistent, and all conservative treatments have been exhausted.
In chronic conditions, the pain experienced by patients is constant and permanent. The cartilage fails to act as an effective buffer between the bones and there is a loss of joint space. The bones rub against each other and cause severe discomfort and pain (especially in the groin area).
In severe degenerative cases, a surgical procedure called a total hip replacement surgery may be performed. The replacement has a lifespan of 15-25 years and has proven to be very beneficial. The surgery carries some risk and should be carefully evaluated.
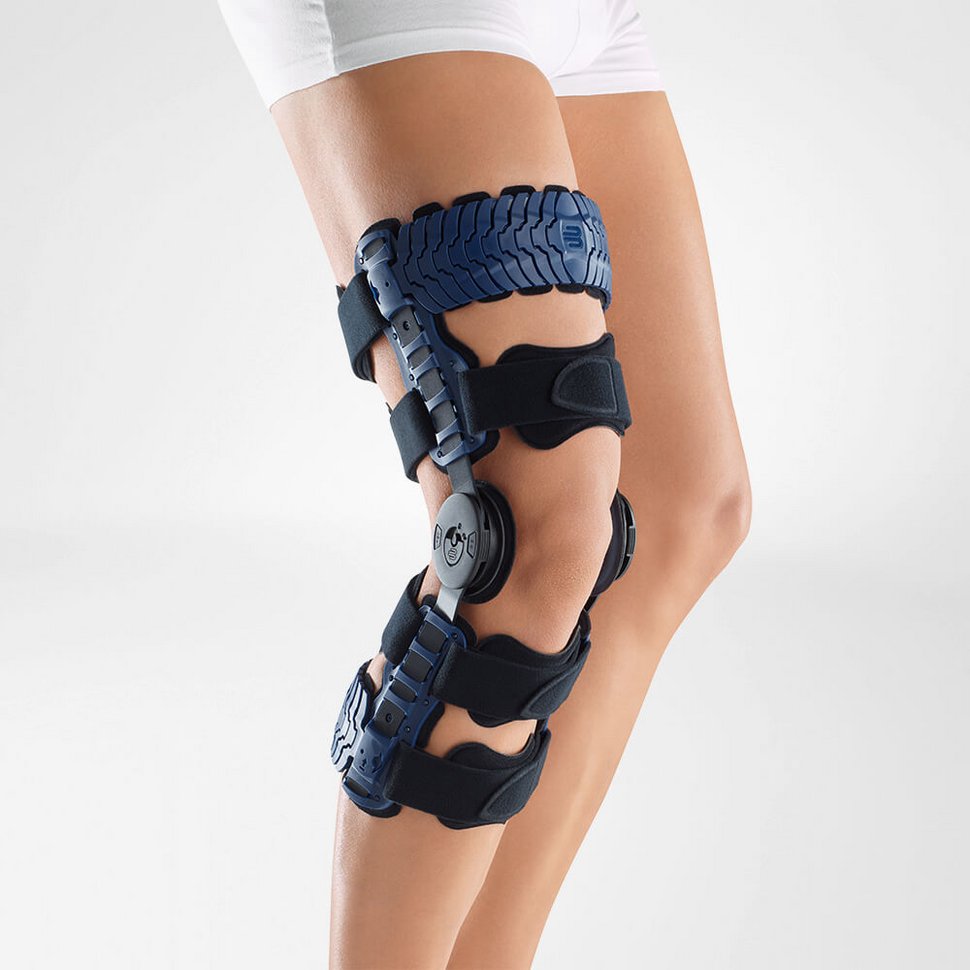
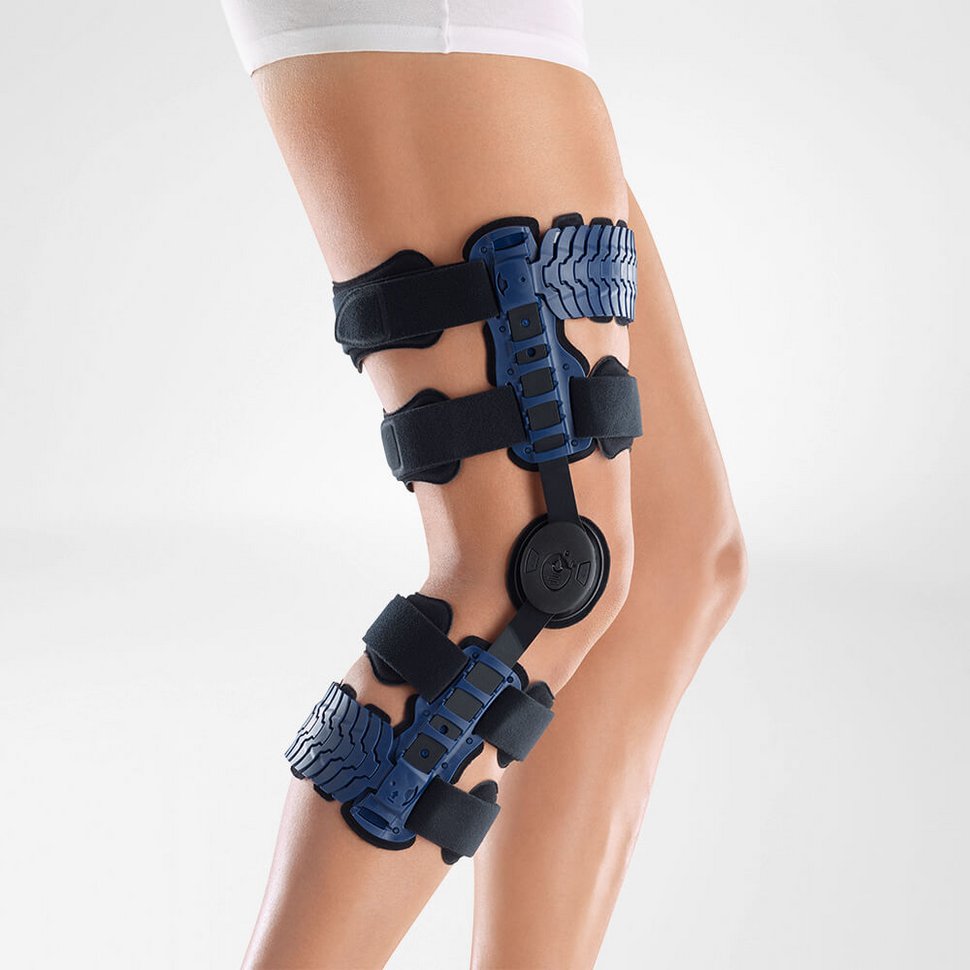
What is the best support brace for hip arthritis?
The CoxaTrain is the perfect brace for hip arthritis, combining the most state of the art technology with slimline lightweight comfort.
Using a pelvic support that stabilizes and unloads the pelvis, it has added cushioning to gently massage the muscles around the hip, reducing pain. Meanwhile the thigh support is connected by a dynamic hinge that follows your anatomical movement to improve your gait and unload the hip itself, alleviating the pain and discomfort that comes with hip arthritis.
An ergonomic design that's easy to put on and take off, it's ideal for being worn under clothes so you can get about your day without thinking about it.
Ideal for sports, exercise and daily life, anyone with hip issues doesn't need to look any further than the CoxaTrain.
-
Relieves pain in the lumbar-pelvis-hip region with the gluteal pad and the two friction pads
-
Relaxes the musculature performing the movement by means of an eccentric joint with a trochanter pad
-
Immediately relieves the pelvis and sacroiliac joints through circular compression using individually adjustable tension straps
-
Height-adjustable thigh bandage via the joint splint
-
High level of therapy compliance thanks to breathable materials and the flat height
Easy to put on thanks to practical finger loops

To support your back after hip pain, we recommend wearing Bauerfeind’s LumboTrain Back Brace which features a gel pad with massaging nubs, which helps to relieve pain in the lumbar region during movement. Produced from a light and breathable material, this back support is fitted to the spine’s natural curvature to provide all day comfort and help with postural adjustment.

References:
* “Controlled trial of a back support (LumboTrain) in patients with non-specific low back pain”, Valle-Jones J., C.; Walsh H.; O´Hara J.; O`Hara H.; Davey N., B.; Medical Consulting Centre; Essex (1992)